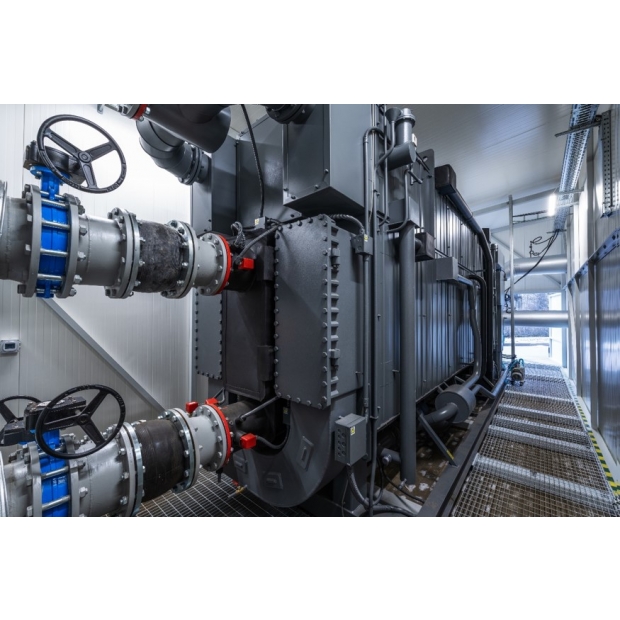
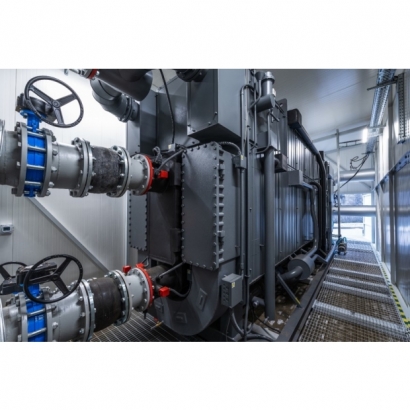
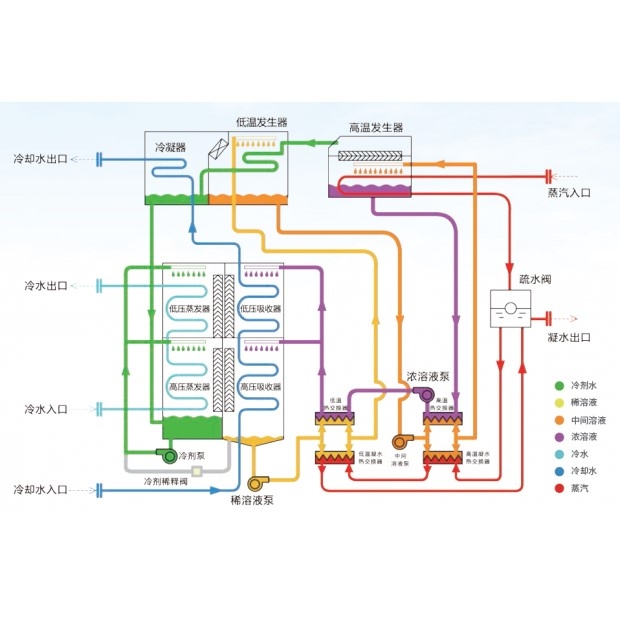
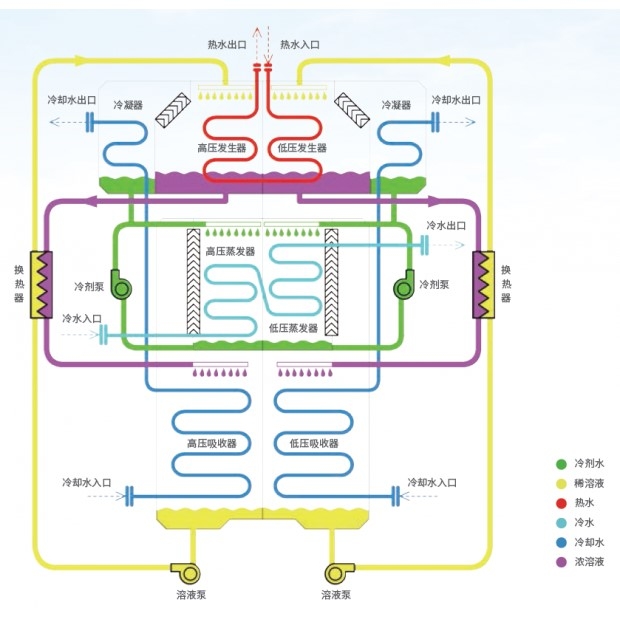
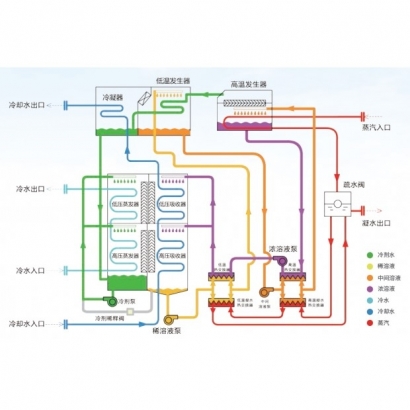
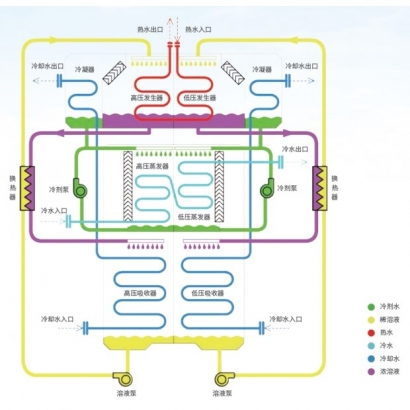
- Evaporator
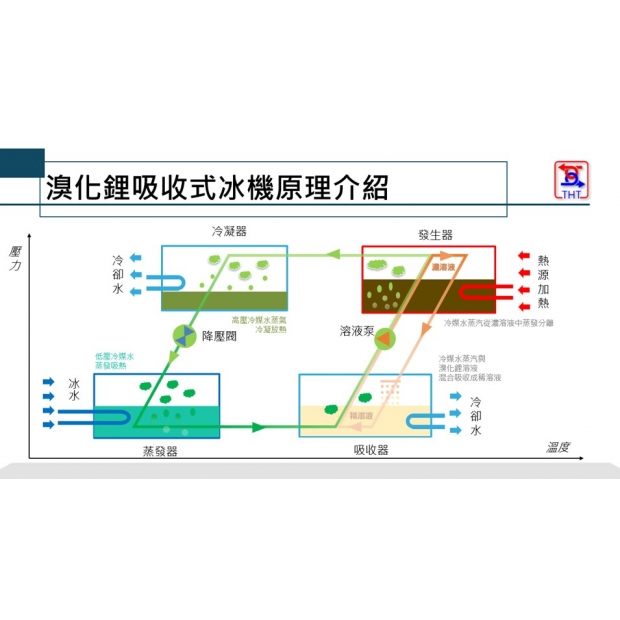
- Condenser
- Generator
- Absorber
Water vapor and concentrated lithium bromide solution are separated in the generator → Vapor condenses into water in the condenser → Throttled to the evaporator for cooling → Absorbed by lithium bromide in the absorber to form a diluted solution → Returned to the generator.
Lithium Bromide Circulation (Replaces Compressor Function):
Concentrated solution from the generator → Pressure reduced via throttling → Absorbs water vapor in the absorber to form a diluted solution → Pumped back to the generator after pressurization.
Advantages:
- Simple structure with minimal mechanical components for stable, low-vibration operation.
- Easy operation with wide cooling capacity modulation from 10% to 100%.
- Compatible with low-grade heat sources such as waste heat, hot water, or steam.
- Driven by thermal energy; power consumption is only 5% of equivalent electric chillers.
- High cooling efficiency under stable heat supply and suitable for automation.
Limitations:
- Lithium bromide solution is corrosive to carbon steel; regular maintenance is required.
- Operates under vacuum; requires excellent sealing. Air leakage may lead to performance degradation.
- High cooling water demand.
- Single-effect hot water type: 30 RT to 3000 RT (also available in two-stage configuration)
- Single-effect / Double-effect steam type: 50 RT to 1500 RT
- Double-effect flue gas type: 100 RT to 1500 RT