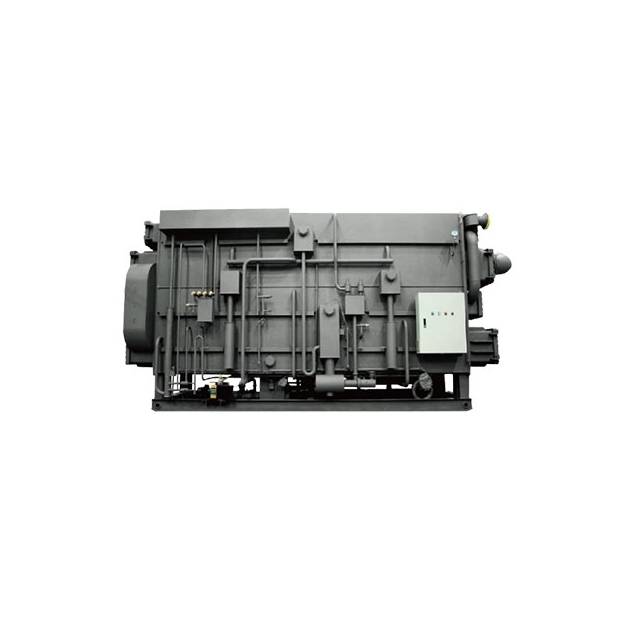
- Evaporator
- Condenser
- Generator
- Absorber
Water vapor and concentrated lithium bromide solution are separated in the generator → The vapor condenses into water in the condenser → Passes through a throttle valve →
Evaporates and absorbs heat in the evaporator → Mixes with lithium bromide in the absorber to form a dilute solution → Returned to the generator.
Lithium Bromide Cycle (Performs the function of a compressor):
Water vapor is separated in the generator, forming a concentrated solution → Pressure is reduced through throttling → In the absorber, the solution absorbs water vapor and becomes a dilute solution → The dilute solution is pumped to increase pressure → Returned to the generator.
Advantages
- Simple structure with few mechanical moving parts; smooth operation and low vibration.
- Easy to operate, with a wide range of cooling capacity adjustment (stepless control from 10% to 100%).
- Low energy quality requirements: steam or hot water-driven units can utilize waste heat, residual heat, or other low-grade heat sources.
- Thermal energy-driven: power consumption is only 5% of that of a mechanical compression chiller with the same cooling capacity.
- Stable cooling efficiency when the heat source is stable, and capable of fully automated control.
- Lithium bromide solution is corrosive to carbon steel, requiring regular maintenance and protection.
- The unit operates under vacuum conditions, requiring high airtightness; air ingress will cause performance degradation.
- Still requires cooling water for operation.
Ø Energy-saving!!! No compressor required!!!
Ø Available waste steam pressure ≥ 30 kPa, or waste hot water temperature ≥ 80°C
Ø Waste heat source capacity > 500,000 kcal/hr (approx. 581 kW)
Ø Or equivalent fluid conditions such as waste gas, exhaust air, or wastewater with the above heat parameters
Ø Cooling capacity demand > 100 RT (≈ 350 kW)
Ø Required chilled water temperature ≥ 5°C
Ø Initial investment is approximately twice that of a conventional mechanical chiller
Ø Available waste steam pressure ≥ 30 kPa, or waste hot water temperature ≥ 80°C
Ø Waste heat source capacity > 500,000 kcal/hr (approx. 581 kW)
Ø Or equivalent fluid conditions such as waste gas, exhaust air, or wastewater with the above heat parameters
Ø Cooling capacity demand > 100 RT (≈ 350 kW)
Ø Required chilled water temperature ≥ 5°C
Ø Initial investment is approximately twice that of a conventional mechanical chiller
Hua Yuan Tai Meng (a subsidiary of MOON-TECH Group)
http://http://www.powerbeijinghytm.com/