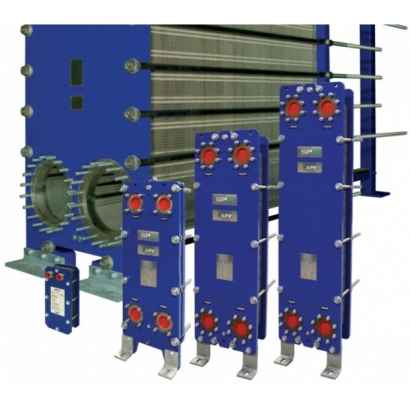
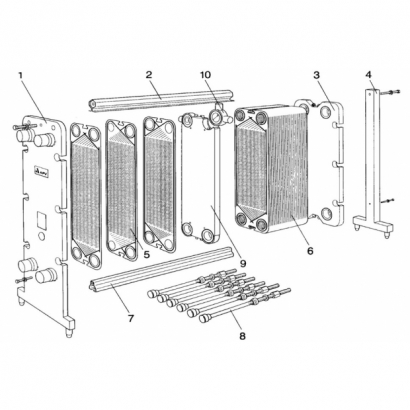
1. Variable Heat Transfer Area with Load: The number of heat transfer plates can be adjusted within the same frame according to the load.
2. Compact Size: The volume is approximately 1/4 to 1/5 of that of shell and tube heat exchangers for the same heat transfer capacity.
3. Lightweight: The weight is approximately half that of shell and tube heat exchangers for the same heat transfer capacity.
4. Cost-effective: Particularly advantageous for counter-current flow, especially in low temperature differential heat transfer scenarios.
5. High Heat Transfer Efficiency: Internal flow fields are typically highly turbulent, resulting in a fouling resistance of only 10% to 25% compared to shell and tube heat exchangers.
Disadvantages of Plate Heat Exchangers (PHE):
Taiwan Heat Transfer can provide:1. Poor Pressure Resistance.
2. Risk of Gasket Leakage.
3. Narrow Passages Prone to Blockage.
• Plate heat exchangers in various materials, including:
316 Stainless Steel, 317L Stainless Steel, 254SMO, AL6XN, Hastelloy, Incoloy, Titanium
• Plate heat exchangers with a variety of certifications, including:
ASME Pressure Vessel Certification, 3A/EHEDG Hygienic Certification for Food Applications,
AHRI Certification for HVAC and Refrigeration, FDA Compliance