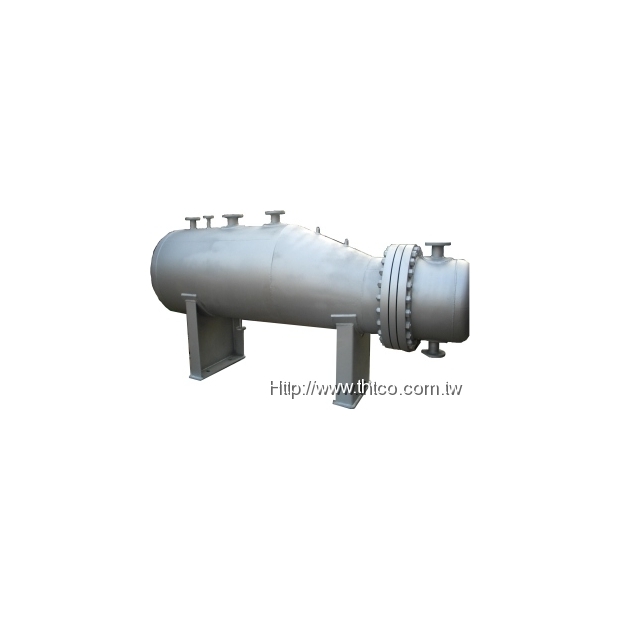
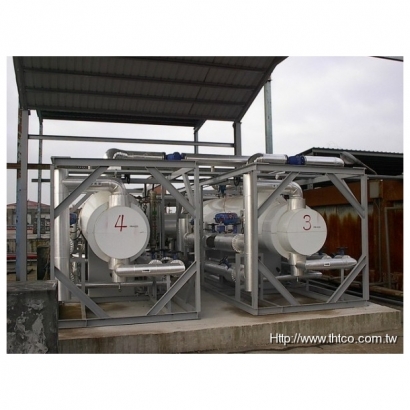
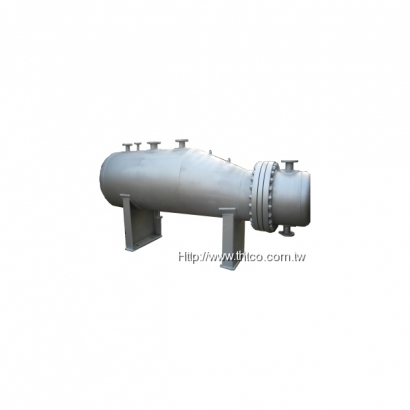
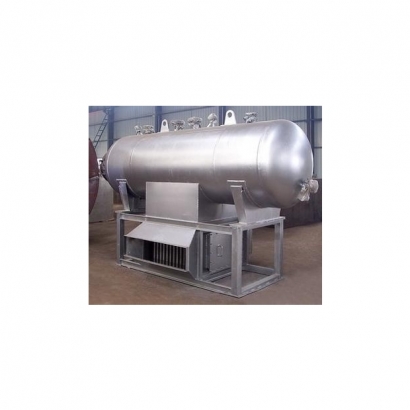
Features
Waste heat boilers generate steam using flue gas or process gas. Unlike conventional heat exchangers, they have the following key characteristics:- Operate under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
- Require control of outlet gas temperature and protection against dew point corrosion.
- Structures and materials must withstand high temperature, high pressure, erosion, and corrosion.
- Must account for scaling and blockage risks in the design process.
Pros and Cons
✔ Advantages
- Energy-saving: Effectively recovers thermal energy from waste gas.
- Compared to other heat recovery equipment, it offers high thermal conversion efficiency and rapid response.
3. Requires strict control of boiler water quality to prevent internal corrosion and scaling.
Design Features
- Dry-out prevention is crucial, especially during startup or low-load conditions.
- Higher evaporation pressure results in better heat transfer efficiency.
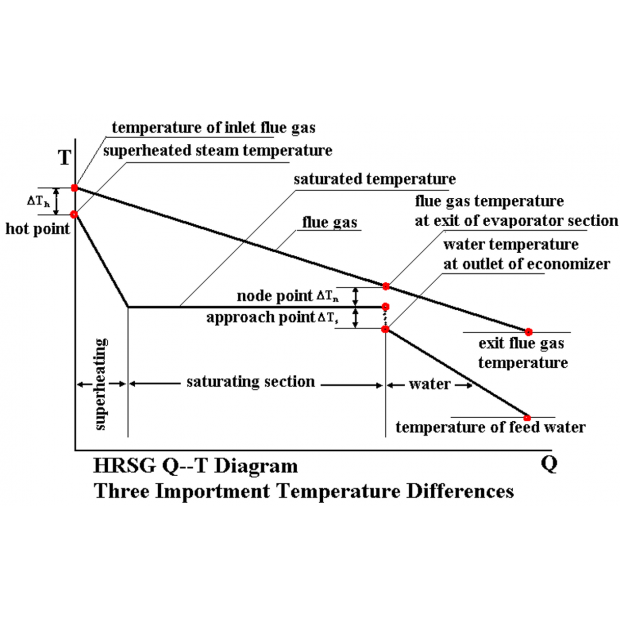
- Inlet gas temperature should be close to the steam saturation temperature to minimize thermal stress.
- Optimal design steam velocity:
– Recommended range: 10–20 m/s
– Excessive velocity may cause erosion and high pressure drop
– Low velocity may lead to unstable flow behavior - Hot point: Approximately 30°C above the steam saturation temperature.
- Pinch Point: Typically 5–15°C
– A smaller temperature difference improves heat recovery but increases equipment cost - Approach Point: Typically 5–12°C
– The economizer outlet temperature should be slightly below the saturation temperature to avoid premature evaporation